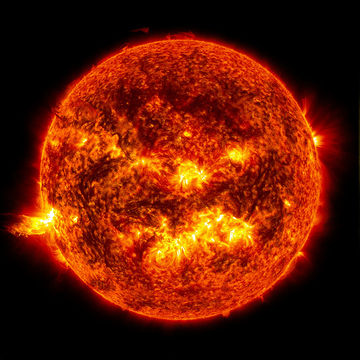
Image credit:-EnergyEducation
The sun is
the head of the solar system and the energy source also. It accounts the 99.99%
of the total mass of the solar system. Its mean distance from the Earth is 1 au ≈ 1.496×108 km
8 min 19 s at light speed. It visual brightness is -26.74 and it
velocity of orbit around the center of the milky way is 220 km,relative to
average velocity of other stars in stellar neighborhood is 20 km and relative to
the cosmic microwave background is 370 km. It equatorial radius is 696,340 km and
it equatorial circumference is 4.379 million km. The surface area is 6.09×1012 km2 12,000 × Earth
and it volume is 1.41×1018 km3 1,300,000 ×
Earth.
History of the sun
The sun is
an ordinary star because there are many smaller stars than larger ones and the
sun is the top 10% by mass. The old name of sun in Greek is Helios and in roman
it says that sol. In sun the hydrogen is 70% and helium is 28% .The change in
sun slowly converts its hydrogen and helium in its core. The outer layer of the
sun is exhibit from differential rotation at the equator of every 25.4 days
near the poles at 36 days. The odd behavior of the sun is not a solid body like
the earth. The similar effects are seen in the gas planets. The rotation extends
down into the interior of sun but its core of the sun rotates from as a solid
body.
General characteristics
The sun
comprises 99.86% of the mass of solar system. The absolute magnitude of the sun
is +4.83 must be estimated to brighter than about 85% of stars in Milky Way
which are red dwarfs. Sun is formed by shock waves from supernovae. This is a
high abundance of heavy elements, such as gold and uranium. This heavy element
could plausibly produced by endothermic nuclear reaction on supernova or
transmutation through neutron absorption with a massive second-generation star.
Sunlight
Image Credit:-DNA India
The solar
constant power is deposits per unit area that is exposed to sunlight. It
constant is equal to 1,368 w/m2 of distance to astronomical unit (AU)
from the sun. Surface of earth is attend by earth atmosphere, so less powers
arrives in clear condition is near the zenith of the sun. The top atmosphere is
composed about 50% infrared light, 40% visible light and 10% ultraviolet light.
Ultra violet radiation ionizes upper atmosphere of day side creating the
ionosphere.
Formation
Image Credit:-Eu-topians
The sun is
formed by gas and plasma. 91% of gas is hydrogen but these gases are converted
into energy in its sun core. This energy is moves out through the
interior layer into the atmosphere of the sun and released in the solar system
as heat and light. Most of the scientist think that the sun and the solar
system are formed for the rotating cloud of gas and dust are called nebula. The
nebula collapsed because the gravity spun faster and flattered into disk.
Structure
Image Credit:-Quora
The
structure formation of the sun is four hydrogen nuclei are fused into one
helium nuclei which are releasing the bunch of energy as photons. It produces
so much heat to melt a block of ice from one mile.
Structures containing the
sun are:-
Image Credit:- Lumen Learning
I)
Core-the innermost part of sun radius is
20-25% while the temperature and pressure are occurring. Hydrogen gas change
into helium which cannot be currently fused.
II)
Radioactive- the surface of sun which cannot occur
until much nearer. The radius of radioactive zone is between 20-25% and 70% zone is transferring by the
radiation which occurs rather than convection.
III)
Tachocline- the boundary region which occur in
radioactive and convection zone.
IV)
Convective zone-the radius of sun about 70% and a
point close to the visible surface. The weather cell which form in the earth
atmosphere.
V)
Photo sphere-the visible surface of the sun is most familiar and
the deepest part of the sun which can directly observe with visible light.
VI)
Atmosphere- the sun atmosphere is composed of several layers of photo sphere,
chromospheres and the corona. The outer layer of sun energy has bubbled up from
its interior layer. Photo sphere is the lowest layer in the sun.
Magnetic activity
I)
Magnetic field-the sun varies magnetic field across
the surface of the sun. The electric current generates a magnetic field inside
the sun and its polar field is 1-2 gauss where the field is typically 3000
gauss in sunspots. The sun magnetic field has two poles south magnetic pole and
north magnetic pole.
II)
Variation in activity-The magnetic fields lead too much effect
called solar activity. The effect of solar activity on the earth includes
auroras at moderate to high latitudes and the disruption of radio
communications and electric power. Solar flares and coronal mass ejections tend
to occur at sunspot groups.
III)
Long term change- Long term change in sunspot number
by related to solar irradiance which in turn for influence for earths long term
climate. Few sunspots were observe during the maunder minimum period and this
coincided time with the era of little ice age.
Heliocentric Theory
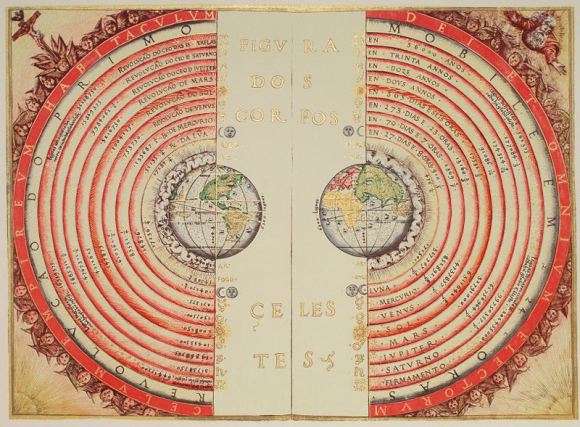
Image Credit:- Phys.org
According to the Heliocentric
theory, the Sun was known to be the centre of the universe but when the image
of the milky way galaxy became clear this theory was proved to be wrong as the
sun was found to be at the outermost corner of the galaxy.
Life phases
Today the sun is roughly
halfway through the most stable part of life. This dramatically has not changed
for over four billion years. Hydrogen fusion core has stopped.
I)
Formation- It formed about 4.6 billion years ago
from collapse and part of a giant molecular cloud consisted hydrogen and helium
to birth other stars. The result of oldest solar system material is consisted
with radiometric date at 4.567 billion years ago. A supernova nearby a
shockwave will have triggered the formation of sun with the molecular cloud and
cause collapse under the own gravity. Gravity and pressure of the cloud
generated a lot of heat in its core and its accreted matter from the
surrounding disk and it trigged the nuclear fusion.
II)
Main sequence- The main sequence of the sun is to
like most stars in the universe during fusion reaction in its core fuse
hydrogen into helium. So it is converted and estimated 100 times of the mass of
earth into helium and solar energy.
Motion and location
I) MOTION IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM- The movement of earth is only possible by the gravitational force of planets. The centre of sun is 2.2 solar radii of the bury centre. Several decades of motion are rather regular forming a tree foil pattern between the periods it appear chaotic. Inner planet of orbit or earth displaces its gravitational force and movement of sun for little effects of relative position of earth and the sun or solar irradiance on earth as a function of time.
Planetary
system
The sun has
eight planets which include some terrestrial planets like (mercury, Venus,
Earth and mars), two giant planets are (Jupiter and Saturn) and two ice giant
planets are (Uranus and Neptune). The comets are a large number of icy bodies
which lie within the orbit of Neptune.
So, how was my post please tell me in the comment section and for more interesting posts follow Kalam Vision and share it also.




0 Comments